You are here: Production
Production of Neodymium-Iron-Boron Magnets
Neodymium Iron Boron is an alloy made mainly from a combination of Neodymium, Iron, Boron, Cobalt and other transition metals, as well as with varying levels of Praseodymium,Dysprosium and Terbium. The exact chemical composition within NdFeB depends on the grade of the NdFeB magnet. Dysprosium and Terbium are added as a replacement for some of the Neodymium to improve the Hci (Intrinsic coercivity) of the “Neo” magnets. An example of a typical composition is given below:
|
Main Elements within NdFeB |
Percentage by weight |
|
Neodymium (Nd) |
15% - 32% |
|
Iron (Fe) |
balance |
|
Boron (B) |
0.90% - 1.2% |
|
Aluminium (Al) |
0.1% - 0.7% |
|
Niobium (Nb) |
0.5% -1% |
|
Praseodymium (Pr) |
0 % - 15 % |
|
Dysprosium (Dy) |
0% - 12% |
|
Terbium (Tb) |
0 % - 3 % |
|
Cobalt (Co) |
0 % - 5 % |
|
Cupper (Cu) |
0% - 0.5 % |
|
Galium (Ga) |
0 % - 0.5 % |
Typical composition of NdFeB alloy

Raw materials: select metals Nd, Dy, Fe-B, Fe, Co, Ga and others for melting
The method for manufacturing Neodymium Iron Boron magnets is as follows:
Melting of the alloy under vaccum
The Neodymium metal element is initially separated from refined Rare Earth oxides in anelectrolytic furnace. The Neodymium, Iron, Boron, and the other chemical elementsare measured out and put in a vacuum induction furnace to form an alloy. Alternatively also prealloys like Dy – Fe or ferro – boron can be used. The mixture is melted due to the high frequency heating.

Strip casting: make Nd-Fe-B alloy to turn into strips of metallic alloy
Strip casting and milling
In simplified terms, the “Neo” alloy is like a cake mixture with each factory having its own recipe for each grade. The resultant melted alloy is then cooled to form ingots of alloy or cooled down by the so-called “strip casting process“. The alloy ingots or the strip cast flakes respectively are then broken down by hydrogen decrepitation (HD) and then jet milled down in a nitrogen and argon atmosphere to a micron sized powder (about 3 microns or less in size). This Neodymium powder is then fed into a hopper, and oriented by a magnetic field in order to allow the pressing of the so-called green compacts of the magnets.

Jet milling: utilize high speed of inert gas flow to make micro particles of NdFeB
Pressing and alignment in magnetic field

There are three main methods of pressing the powder: isostatical pressing, axial pressing and transverse pressing. Die pressing requires tooling to make a cavity that is slightly larger than the required shape (because sintering causes shrinkage of the magnet). The Neodymium powder enters the die cavity from the hopper and is then compacted in the presence of an externally applied magnetic field. The external field is either applied parallel to the compacting force or perpendicular to the direction of compaction. Transverse pressing gives higher magnetic properties for the NdFeB sintered magnets.
The other method of pressing is isostatic pressing. The NdFeB powder is put into a rubber mould and is put into a large fluid-filled container which then has the pressure of the fluid increased. Again, an external magnetizing field is present, but the NdFeB powder is compacted from all sides. Isostatic pressing gives the best possible magnetic performance for Neodymium Iron Boron. The methods employed vary depending on the grade of “Neo” required and are decided by the manufacturer.
The external magnetizing field is created by a solenoid coil set on either side of the compacting powder. The individual powder particles of the NdFeB powder align with the magnetizing field that is applied – the more homogenous the applied field, the more homogenous the magnetic performance of the Neodymium magnet. As the Neodymium powder is pressed by the die, the direction of magnetization is locked in place – the Neodymium magnet has been given a preferred direction of magnetization and is called anisotropic. Rare Earth magnets exhibit uniaxial magnetocrystalline anisotropy, i.e. they have a unique axis crystal structure corresponding with the easy axis of magnetization. In the case of Nd2Fe14B, the easy axis of magnetization is the c-axis of the complex tetragonal structure. In the presence of an external magnetizing field, it aligns along the c-axis, becoming capable of being fully magnetized to saturation with a very high coercivity.
Sintering and annealing
The ‘green’ Neodymium magnet is then sintered to give it its final magnetic properties. The sintering process is carefully monitored (a strict temperature and time profile has to be applied) and occurs in vacuum or in an inert (oxygen-free) atmosphere (e.g. argon). If oxygen is present, the resultant oxides destroy the magnetic performance of the NdFeB. The sintering process also causes shrinkage of the magnet as the powder fuses together. The shrinkage gives a magnet close to the required shape but the shrinkage is usually uneven (e.g. a ring may shrink to become an oval). At the end of the sintering process a final rapid quench is applied to rapidly cool the magnet. This is to minimize the unwanted production of other magnetic phases. A rapid quench maximizes the magnetic performance of NdFeB. Because the sintering process causes an uneven shrinkage, the shape of the Neodymium magnet will not be to the required dimensions.

Sintering: utilize vacuum sintering furnaces to develop the magnetic properties by an aging heat treatment
Machining
The next stage is to machine the magnets to the required tolerances. Because machining is required, the Neodymium magnets are made slightly larger when being pressed, e.g. larger outer diameter, smaller inner diameter and taller for a ring magnet. Standard magnet dimensional tolerances are +/-0.1mm although +/-0.05mm is achievable at extra cost. The possibility of even tighter tolerances depends on the shape and size of the magnet and may not be achievable. For note, the Neodymium magnet is very hard. Trying to cut holes in NdFeB with a standard drill or carbide tip will blunt the drill bit. Diamond cutting tools (CNC diamond grinding wheels, diamond drills, etc.) and wire cutting machines (EDM) have to be used. The NdFeB swarf powder produced during machining needs to be cooled by liquid otherwise it may spontaneously combust. For Neodymium block magnets, there may be cost savings in using much larger magnet blocks made by isostatic pressing and cutting them into smaller Neodymium blocks of the desired size. This is done for speed and for mass production (where enough cutting and grinding machines are present) and is known as “slice and dice”.
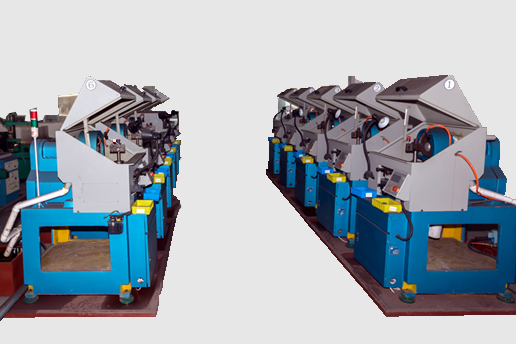
Machining: use mechanical equipment to make the accurate dimensions and shapes
Coating
Once the final dimensions for the magnet has been met by machining, the Neodymium magnet is given a protective coating. This is usually a passivation of the surface or a Ni-Cu-Ni coating. Other coatings may be possible. It is not recommended to use the magnet without any protective layer.
©2016 Copyright by Ningbo Haishu Magnet Maxwell Co., Ltd. All rights reserved.